Architectural Design
Usage
Docopt language
To define the cli interface of AutoDev, docopt command definition language will be used.
The following is a summary of the language constructs used in AutoDev’s definition
The docopt language defines the ‘help message’ of a command to define it’s usage and options.
Usage pattern is a substring of the help message that starts with ‘usage:’ (case insensitive) and ends with a visibly empty line.
The first word after usage: is interpreted as the command’s name, e.g.:
"""
Usage: simple_program.py
"""
The usage defines:
- Optional elements are specified within square brackets, e.g.:
program.py [optional-argument] - Arguments are specified with upper-case words, e.g.
program.py ARGUMENT
Every line that starts with - or -- defines an option for the command, e.g.: -o or --option
Synonymous short and long options can be defined on the same line, separated by a comma, e.g.: -o, --option
Two spaces can be used to separate an option from it’s informal description, e.g.: -o Informal description.
Default values for arguments can be defined with the following form: [default: value]
AutoDev usage definiton
The usage of AutoDev’s command autodev is defined as follows, using docopt command definition language:
"""AutoDev
Usage:
just run [PATH-TO-PROJECT] [-q | --quiet] [-d | --direnv] [-m MODEL-NAME] [-p PROMPT-FILE-PATH]
just run -l | --list
Generates development environment configuration for a project.
Use `nix develop` to start development environment.
Options:
PATH-TO-PROJECT Path to the project the dev env is for. [default: ./]
-h, --help Display help message.
-q, --quiet Disable prints.
-d, --direnv Generate .envrc file also.
-m MODEL-NAME, --model MODEL-NAME Model to use to generate the config. [default: llama3]
-l, --list List available and installed models.
-p PROMPT-FILE-PATH, --prompt PROMPT-FILE-PATH Custom prompt file path.
"""
Development
To enter AutoDev’s development enviroment:
nix develop
Just is used to simplify running commands.
To see available commands:
just
Custom Prompt
Generation Halting
The user can halt the generation of the development environment in any moment by pressing ctrl + C on their keyboard.
This is inline with the behaviour of most command line tools.
Modules
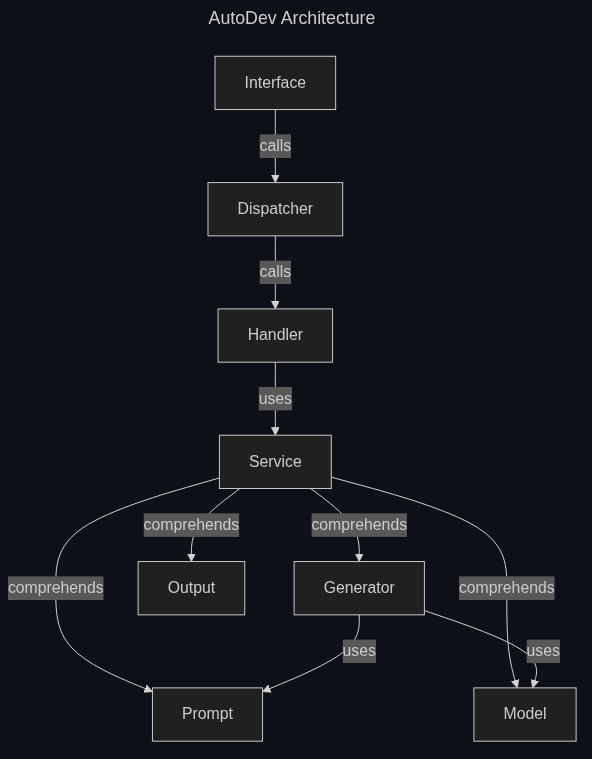
The source code organized in the following modules:
- Interface: responsible for defining command api and related command parsing, similar to a View in MVC architecture;
- Dispatcher: responsible for linking the command arguments to the correct execution of handler functions;
- Handlers: responsible for handling high level command operations;
- Services: responsible for defining business logic common to multiple handlers;
- Generator: responsible for generating dev env config;
- Prompt: responsible for defining prompt formats to be passed to LLMs;
- Model: responsible for wrapping the LLM service;
- Output: responsible for generating output, be it in file or cli print format.
| Back to index |
| Previous Chapter |
| Next Chapter |